Meta Description
The meta description sits below the meta title in search results, offering a concise webpage summary to entice readers to click and explore the page's content.
What is a Meta Description?
A meta description is an HTML attribute that summarizes a webpage's content succinctly. This snippet, typically 155–160 characters in length, is showcased on search engine results pages (SERPs) beneath the meta title. Although not a direct ranking factor, an alluring meta description can considerably enhance click-through rates, making it a linchpin in driving organic web traffic and refining user experience.
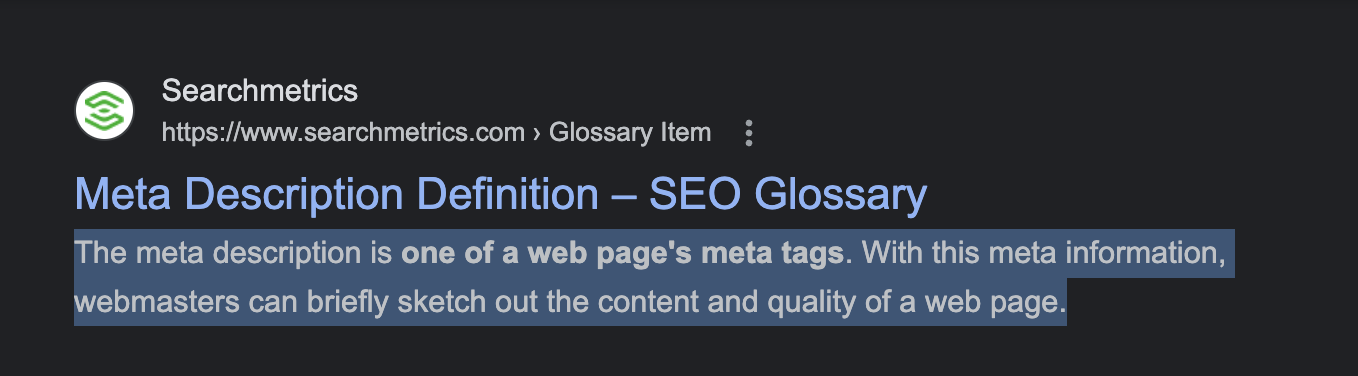
Here is how it looks on the SERPs:
How to Implement the Meta Description
The meta description resides in the <head> section in a web page's HTML structure. Below is an example:

Meta Descriptions and Their Importance in SEO
- Increased Click-Through Rate (CTR): An engaging meta description can significantly boost your CTR from SERPs, which search engines can interpret as your site offering valuable content.
- Keyword Relevance: Integrating relevant keywords (not stuffing) can highlight relevance to user queries.
- Enhanced User Experience: A concise overview helps users assess the page’s relevance to their intent.
Why Does a Meta Description Matter?
- Tempt the Searcher: A compelling description can persuade users to click even if it’s not the top result.
- Convey Core Content: It lets users assess the relevance of your page to their query.
- Indirect SEO Gains: Higher CTR may send positive signals to search engines about your page’s value.
Do's and Don'ts of Meta Descriptions
✅ Do's- Be Descriptive: Accurately and enticingly reflect the page’s content.
- Weave in Keywords: Use relevant keywords naturally to stand out in SERPs.
- Maintain the Right Length: Keep within 155–160 characters to avoid truncation.
- Shun Duplication: Every page should have a unique meta description.
- Refrain from Keyword Overindulgence: Avoid spammy or keyword-stuffed phrasing.
Good vs. Bad Meta Description Examples
Good Descriptions:- "Unravel the myriad perks of vegan chocolate cake and dive into recipes that satiate your sweet cravings."
- "Our 2023 compendium presents detailed reviews on premier running shoes, guiding you to ergonomic comfort and style."
- "Grasp expert insights on cultivating roses in temperate zones, promising year-round floral exuberance."
- "Vegan, Cake, Chocolate, Best Recipes, Tasty Vegan Cake, Delicious Chocolate."
- "Welcome to our main website page."
- "Open and read this."
Conclusion
A meta description, though brief, can significantly influence a user's decision to engage with your content. When optimized adeptly, it is a formidable tool, propelling organic traffic, bolstering user engagement, and indirectly enhancing SEO metrics.
FAQs on Meta Description
While not directly, a compelling meta description boosts CTR, which can indirectly benefit SEO.
Optimally, maintain a 155–160 character length to prevent it from being cut off in SERPs.
Search engines might auto-generate one using the page content, but custom crafting ensures accuracy and engagement.
A strong meta description is clear, compelling, and concisely summarizes a page's content, enticing users to click.
In SEO, the meta description is a brief summary of a webpage's content displayed beneath the title in search results.
The meta description appears in SERPs below the title and can be viewed in a page's HTML within the <head> section.
